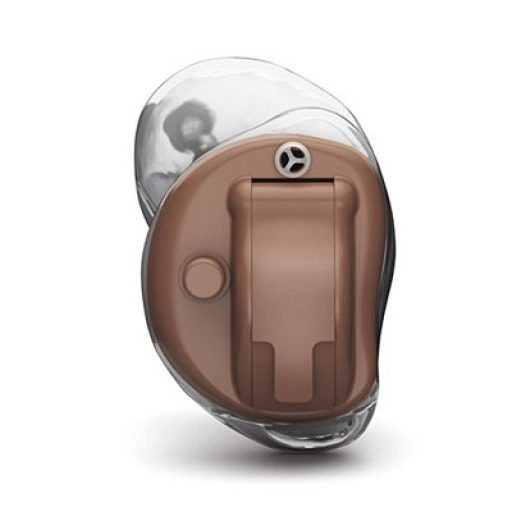
Causes of Hearing Loss
Although age (presbyacusis) is considered to be one of the primary causes for hearing loss this is not necessarily always the case.
Hearing loss (temporary or permanent) can occur at any time and may be as a result of any of the following:
Acquired hearing loss
● Physical trauma – blow to the head
● Noise trauma – exposure to steady rate of noise
● Acoustic trauma – exposure to repeated loud sounds such as gun fire
● Blast injury – explosions
● Barotrauma – pressure changes due to flying or diving
● Miscellaneous – radiation exposure, electric shock
● Surgical e.g. poor ear syringing techniques, post surgery operations such as a stapedectomy
● Pharmacological – certain drugs
● Viral – measles, mumps, herpes zoster (shingles)
● Bacterial – upper respiratory infections e.g. colds & flu which can lead to middle ear infections
● Fungus – Otomycosis (fungus in the outer ear)
● Parasitic – meningitis
● Cancer of the middle ear, leukaemia, vestibulocochlea schwannoma (acoustic neuroma)
● Hormonal – Myxodema (hypothyroidism), diabetes, acromegaly – can cause excessive growth in children or soft tissue growth in adults
● Others – Dyslipidaemia (too much fat in the blood), hyperuricaemia (gout-excessive uric acid in blood), renal failure where kidneys cannot cleanse body of impurities, causing toxicity
● Arteriosclerosis (hardening of the arteries), hyper-tension (high blood pressure), other circulatory disorders
● Wegenet’s granulomatosis (bone lesion), polyarteritis nodosa (disease of artery wall), Bechets Syndrome
● Ototoxic substances not iatrogenically introduced such as carbon monoxide, tobacco and alcohol
● Meniere’s disorder
Congenital hearing loss
● Genetically (some 50-60% of all cases are hereditary) – Osteo genesis imperfecta (brittle bones), ushers syndrome, gargoylism (skull/facial deformities), Waardenburgs syndrome, Treacher Collins syndrome, Allports syndrome, Paget’s disease (softening of the bones with age), hereditary presbyacusis. The most common form of hereditary hearing loss is otosclerosis (restriction of middle ear bone movement)
● Pre-natal maternal rubella – Mother contracts German Measles during pregnancy
● Cyto megalovirus (CMV) – Mother contracts this herpes like virus with flu type symptoms
● Ototoxicity
● Congenital syphilis
● Premature birth
● Anoxia – oxygen deficiency at birth e.g. umbilical chord twisted around baby’s neck
● Birth Trauma – damage by forceps during delivery
● Rhesus incompatibilities – Rhesus factors in father’s & mother’s blood can cause jaundice
Get a free hearing test with one of the UK's best hearing care specialists

Book a FREE hearing test

FREE online hearing test
Find your nearest clinic

