Types of Hearing Loss
Conductive hearing loss
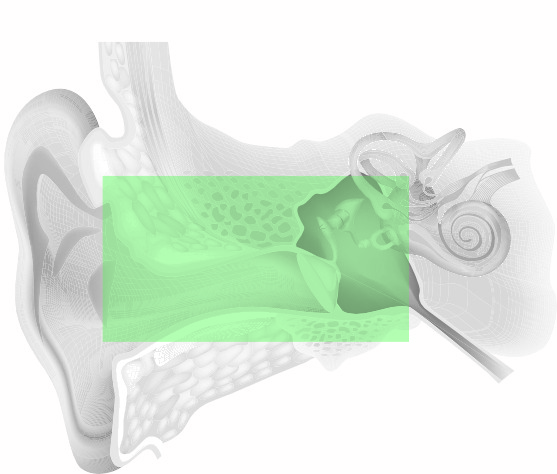
Is a disorder of the outer and/or middle ear, whereby sound is not properly reaching the hearing nerve. With this type of loss the individual may hear better in background noise (paracusis), they may not be able to hear their own voice so well and as a consequence may speak quietly. Generally, increasing volume will increase the clarity. This is commonly treated medically or through ear surgery. However, if the conductive loss is permanent, properly fitted hearing instruments such as spectacle hearing aids can often alleviate the problem.
Sensori-neural hearing loss (nerve deafness)
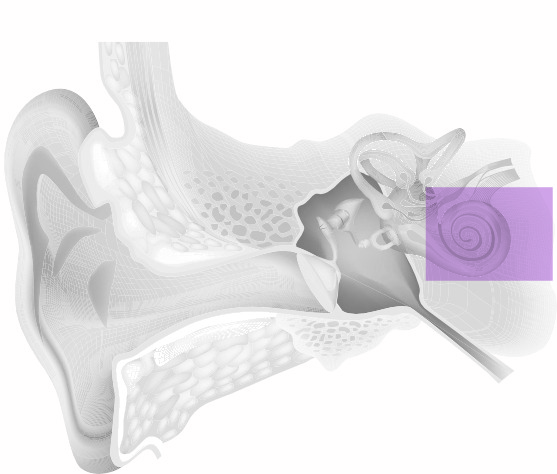
Is a disorder of the inner ear, whereby the nerve endings are not transmitting electrical impulses properly due to damage to the hair cells in the cochlea (this is typically the most common type of hearing loss). With this type of loss the individual tends to hear worse in background noise; they tend to speak louder as they cannot hear their voice properly.
They may also complain of poor discrimination i.e. one word runs into another. An increase in volume will not necessarily increase clarity. They may also hear some sounds better than others, e.g. male voices better than female voices or low frequency sounds better than high frequency sounds. Modern digital technology will enable most people with a sensori neural hearing loss to be significantly helped.
Mixed hearing loss
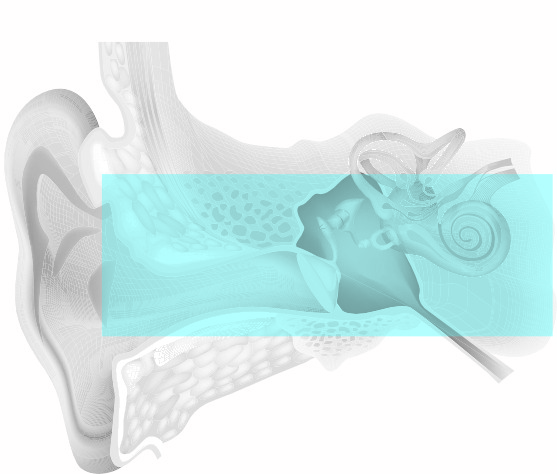
Contains elements of both of the above.
Central hearing loss
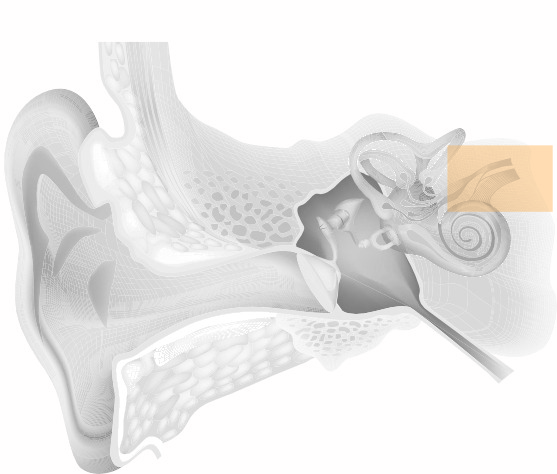
This is caused by damage to the auditory nerve or hearing centres. Sound waves are transmitted normally through the ear, however, the auditory nerve may not be able to send the electrical impulses to the brain, or the hearing centres of the brain may not receive the signals correctly. Typical symptoms may be detecting sound but not being able to understand or process it.
Get a free hearing test with one of the UK's best hearing care specialists

Book a FREE hearing test

FREE online hearing test
Find your nearest clinic

